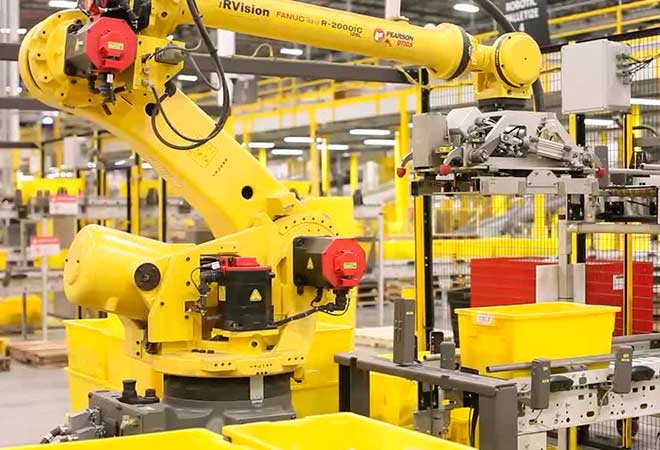
Amazon Robotics is an innovative moving technology that has helped millions of people order goods from Amazon. Typically, in a distribution center, packages are transported along a conveyor line or using machines operated by humans (for example, forklifts). Under Amazon Robotics' approach, all items are placed on mobile devices. As soon as the order enters the database, the software detects the nearest automated controlled robotic device to the article and sends it to pick up the goods. Hundreds of orders are processed daily at the fulfillment centers. A growing portion of these packages is picked, sorted, and distributed by Amazon's Robin robot picker.

A new phone model that will run on solar power will integrate with Starlink satellite systems and will work even on Mars, information sources claim. Tesla, the world''s biggest electric car maker, is reportedly developing a futuristic smartphone that could. Regardless of the rumors, what the Texas-based company is doing is maintaining complete confidentiality regarding the alleged device. The corporation still does not confirm its production plans and keeps information about the development of the product in secret.

As demand for robots grows, companies in numerous industries are looking for additional ways to increase their productivity and competitiveness in the post-pandemic era. ABB has developed a series of long-term forecasts looking at the key factors affecting demand for robots in the coming year. With artificial intelligence (read more here) now demonstrating near-human capabilities, the pandemic has intensified global processes, from labor shortages and supply chain instability to customer individuality and the growing need for resiliency. It has led companies to turn to robotic automation increasingly. As technology provides new opportunities for buyers to meet their needs, the latest trends will continue to emerge, driving demand in areas where robots have not typically been used.

Like the billion installed in any smartphone used today, traditional picture cameras record the saturation of light and the color gamut. Based on standard off-the-shelf camera technology called CMOS, these cameras are getting smaller and more powerful every year and now have a resolution of a few dozen megapixels. However, they can only see in two dimensions, creating a flat, drawing-like image.
Scientists at Stanford University have developed a way to allow ordinary image sensors to perceive three-dimensional light. In other words, it will soon be possible to measure the distance to objects with these conventional cameras.
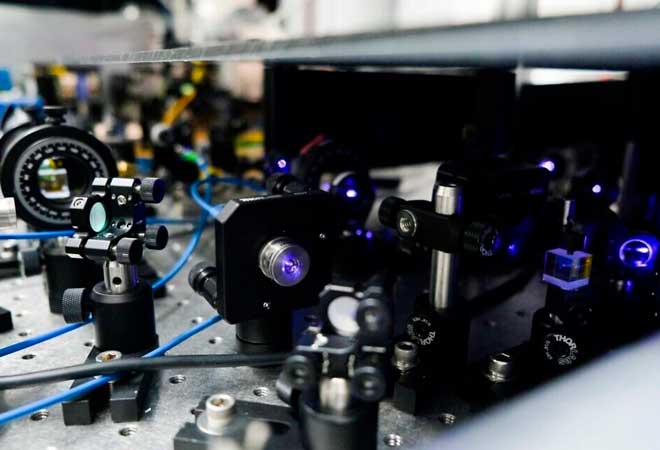

Israeli engineers created the country's first quantum computer: What are its features?
What is a quantum computer? Computers, as we know, store data in binary code, and the smallest unit of information storage is the bit. It can only take one of two values: 0 or 1. In solving a problem, a computer performs many consecutive operations on bits, and in the case of complex issues, this takes a lot of time. Quantum computers work radically differently from classical computers. To solve any algorithmic problems, they use quantum bits-cubits.

One hundred years ago, Karel Čapek coined the word "robot". Now a robot has written a play dedicated to Čapek himself.
Fantastic movies about the future at the end of the last century often have a story about new-age robots in the plot. Usually, artificial intelligence begins to operate on Earth despite its owners, people. And as is often the case, scenarios are transferred from paper to real life. Before humanity could even blink an eye, robots became an everyday occurrence.